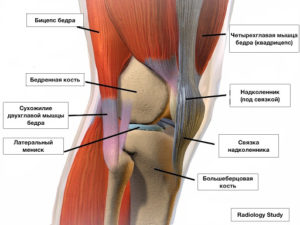
KNEE ANATOMY
Edema of the knee joint is usually associated with fluid spilling into the joint capsule, that is, the shell that protects and wraps the knee joint.
The joint capsule of a healthy knee contains as much synovial fluid as is needed to nourish the joint and reduce friction.
In a swollen knee, the fluid contained in the capsule is present in more than necessary and can be of two types:
- synovial fluid
- Bloody fluid
Bloating due to trauma
The presence of blood fluid is a sign that the cause of the effusion should be identified in the event of trauma, such as a ruptured ligament (it is usually the anterior cruciate ligament that causes major problems of this type, accompanied by inability to bend the leg), or tearing the meniscus.
If the joint is damaged, there will be sudden blood spills and the knee tends to turn red, accompanied by a rise in temperature.
Bloating due to inflammation
The presence of synovial fluid in a swollen knee is of inflammatory origin, which can occur in both acute and chronic forms.
Osteoarthritis and arthritis are chronic inflammatory conditions, and swelling often occurs after doing quite strenuous physical activity, such as running after a worn knee.
A condition in which the knee swells chronically is called synovitis.
Tendinitis and bursitis are among the acute inflammatory diseases. Causes of a swollen knee can also be associated with certain medical conditions, such as gout, brucellosis, and Lyme disease.
Behind the knee
A single swelling behind the knee can be caused by a cyst called Baker’s cyst, an alternating disorder that, in some cases, also results in difficulty moving the joint. It often affects knee joints that are already prone to osteoarthritis, and its treatment is conservative and rarely requires a surgeon’s intervention.

DIAGNOSTICS OF FAILURE REASONS
It will obviously be more convenient to start with an injury assessment to try to “diagnose” what type of payment it is, even if the solutions for quick pain relief are the same, while for medical treatment it is always a good idea to contact a specialist or your general practitioner practitioner who can then indicate the most appropriate action. It is advisable to see a doctor if the swelling persists within 2/3 days.
NATURAL REFINING CARE
If the pain is weak, you can resort to PRICE-therapy: protection, rest, ice, compression, increase.
To reduce edema, it is necessary to reduce effusion by applying ice, which should be applied as soon as possible.
On There are also clay preparations or elastic bandages on the market that are useful for compressing and relieving swelling.
It is also advisable to hold the limb while resting and lifting horizontally, trying to weigh the weight gain and possible obesity.
ANTIPLAMMATOR TREATMENTS FOR PAIN
NSAIDs are provided as a guarantee of rapid pain relief due to the irritating side effects of systemic formulations (oral, intramuscular). Steroids) based on diclofenac in topical forms such as gels, creams or foams. These drugs are found in pharmacies in varying concentrations from 1% to 4%, as well as in different forms.
According to some clinical studies, the most effective is that in a gel spray, which, thanks to nanomellar technology, is able to transfer the active principle (diclofenac) deep into the target site, providing fast and long-lasting pain relief and inflammation reduction.



